前言
起初动机完全是面试问到这个问题了,觉得需要了解下。
看别人对源码的解读,完全不知道如何去表达,直到看了手写IOC,再去看源码,觉得哦…
Spring 容器高层视图
Spring 启动时读取应用程序提供的 Bean 配置信息,并在 Spring 容器中生成一份相应的 Bean 配 置注册表,然后根据这张注册表实例化 Bean,装配好 Bean 之间的依赖关系,为上层应用提供准 备就绪的运行环境。其中 Bean 缓存池为 HashMap 实现。
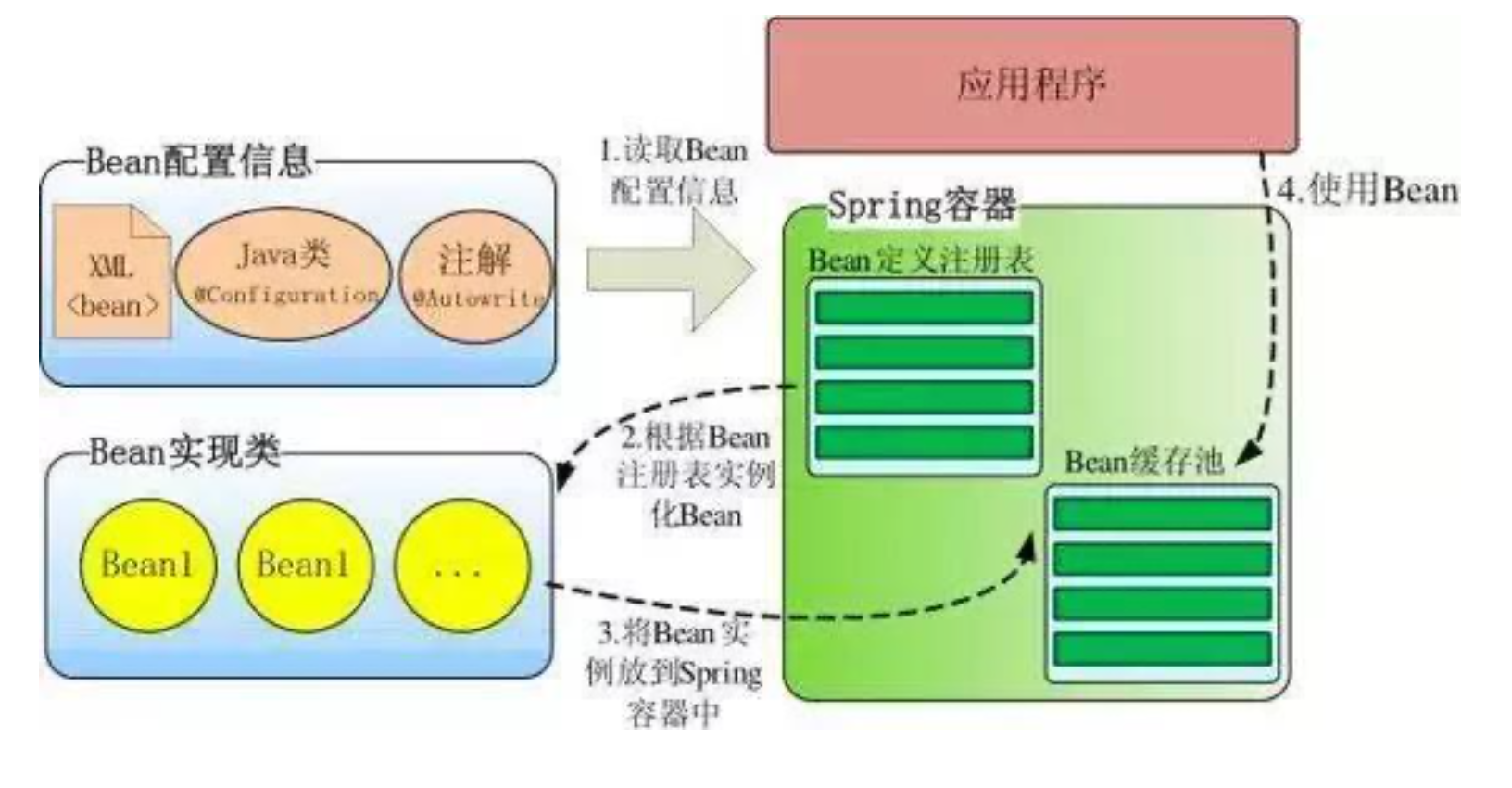
IOC流程
- 初始化IOC容器。定义一个BeanFactory,对象实例的工厂,这个工厂提供一个统一的方法,getBean
- 扫描包路径,读取配置文件,或者扫描注解。将配置信息转换为IOC容器能够识别的数据结构(BeanDefinition),并注册到工厂
- 调用BeanFactory.getBean() 会触发Bean的实例化。(反射)
手写IOC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Documented
@Target({ ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Documented
@Target({ ElementType.FIELD })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Autowired {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| @Component
public class UserService {
public User getUser() {
return new User("admin", "123456");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| @Component
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void say() {
User user = userService.getUser();
System.out.println(user);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class BeanDefinition {
private Object bean;
private Class<?> beanClass;
private String className;
private boolean lazyInit;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface BeanFactory {
Object getBean(String name);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
| public class ApplicationContext implements BeanFactory {
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<>();
private Map<String, Object> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public ApplicationContext(String basePackage) {
doScan(basePackage);
doIoc();
doDI();
}
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) {
return doGetBean(name);
}
private Object doGetBean(String beanName) {
return beanMap.get(beanName);
}
private void doScan(String basePackage) {
URL resource = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(basePackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File basePackageFile=new File(resource.getFile());
File[] files = basePackageFile.listFiles();
for (File file: files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
doScan(basePackage + "." + file.getName());
} else if (file.isFile()) {
classNames.add(basePackage + "." + file.getName().split("\\.")[0]);
}
}
}
private void doIoc() {
if (classNames.size() <= 0) {
return;
}
for (String className: classNames) {
try {
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component component = cls.getAnnotation(Component.class);
Object instance = cls.newInstance();
if (StringUtils.isBlank(component.value())) {
beanMap.put(camelCaseName(cls.getSimpleName()), instance);
} else {
beanMap.put(camelCaseName(cls.getSimpleName()), instance);
beanMap.put(component.value(), instance);
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void doDI() {
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry: beanMap.entrySet()) {
Field[] fields = entry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field:fields) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
Object obj = null;
if (beanMap.containsKey(field.getName())) {
obj = beanMap.get(field.getName());
} else {
obj = beanMap.get(camelCaseName(field.getType().getSimpleName()));
}
if (null == obj) {
return;
}
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(entry.getValue(), obj);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
private static String camelCaseName(String s) {
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
String firstChar = String.valueOf(chars[0]);
chars[0] = firstChar.toLowerCase().charAt(0);
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class IocApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new ApplicationContext("com.idcmind.ioc");
UserController componentB = (UserController) ctx.getBean("userController");
componentB.say();
}
}
|
实际过程中Bean是懒加载的,延时实例化。
当我们需要UserController的时候,会检索到需要先实例化UserService。
这就是依赖注入吧。当然,这样调用的时候需要全类名。
实现如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
| public class ApplicationContext implements BeanFactroy {
private Map<String, Object> beanMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private ConcurrentHashMap<String,BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private List<String> packageNames = new ArrayList<>();
public ApplicationContext(String basePackage) throws Exception {
scanBasePackage(basePackage);
registerBeanDefinition(packageNames);
}
private void registerBeanDefinition(List<String> packageNames) throws Exception {
if (packageNames.size() <= 0) {
return;
}
for (String packageName : packageNames) {
Class<?> c = Class.forName(packageName);
if (c.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setClassName(c.getName());
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(c);
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(true);
beanDefinition.setBean(c.newInstance());
beanDefinitionMap.put(c.getName(), beanDefinition);
}
}
}
private void scanBasePackage(String basePackage) throws Exception{
URL resource = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(basePackage.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File basePackageFile=new File(resource.getFile());
File[] files = basePackageFile.listFiles();
for (File file: files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
scanBasePackage(basePackage + "." + file.getName());
} else if (file.isFile()) {
packageNames.add(basePackage + "." + file.getName().split("\\.")[0]);
}
}
}
public Object getBean(String name) throws Exception {
return doGetBean(name);
}
private Object doGetBean(String beanName) throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Objects.requireNonNull(beanName, "beanName不能为空");
Object instance = beanMap.get(beanName);
if(instance != null){
return instance;
}
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
String className = beanDefinition.getClassName();
Class<?> cls = Class.forName(className);
instance = cls.newInstance();
setField(instance);
beanMap.put(beanName, instance);
return instance;
}
private void setField(Object instance) {
Field[] fields = instance.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field: fields) {
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)) {
String filedName = field.getType().getName();
try {
Object fieldBean = getBean(filedName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(instance, fieldBean);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
|
最后
本文到此结束,感谢阅读。如果您觉得不错,请关注公众号【当我遇上你】,您的支持是我写作的最大动力。



