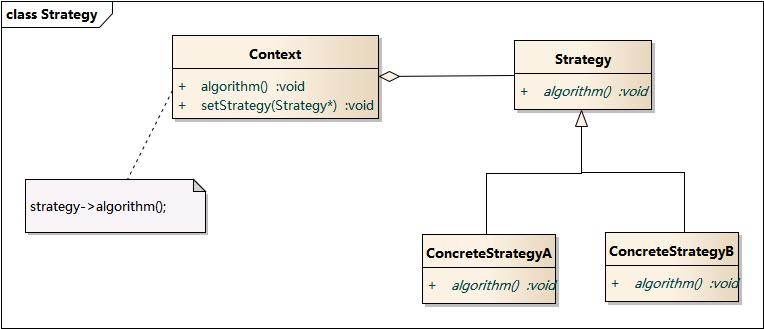
策略模式(Strategy Pattern)是比较典型的对象行为型模式,它是将对处理对象的一系列不同算法都单独抽离出来,单独封装成一个个类。策略的出现,主要是为了解决不同算法替换时的逻辑判断,将逻辑判断移到Client中去(即由客户端自己决定在什么情况下使用什么具体策略) 。
策略模式包含如下角色:
Context: 环境类,也叫做上下文角色,起承上启下封装作用; 屏蔽高层模块对策略、算法的直接访问,封装可能存在的变化.
Strategy: 抽象策略类,策略、算法家族的抽象,通常为接口,定义每个策略或算法必须具有的方法和属性
ConcreteStrategy: 具体策略类,实现抽象策略中的操作,含有具体的算法
在以下情况下可以使用策略模式:
如果在一个系统里面有许多类,它们之间的区别仅在于它们的行为,那么使用策略模式可以动态地让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为。
一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种。
如果一个对象有很多的行为,如果不用恰当的模式,这些行为就只好使用多重的条件选择语句来实现。
不希望客户端知道复杂的、与算法相关的数据结构,在具体策略类中封装算法和相关的数据结构,提高算法的保密性与安全性。
学习设计模式就是为了写出更加优雅的代码, 然而很多时候项目中不知道在什么场景下用什么设计模式合适。这里提供几个案例, 让大家在实践中去理解应用, 去悟道。
首先最经典的就是JDK中排序器的应用了。
策略接口
1 2 3 4 5 @FunctionalInterface public interface Comparator <T > int compare (T o1, T o2) ... }
具体策略类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class AscComparator implements Comparator <String > @Override public int compare (String o1, String o2) return o1.compareTo(o2); } }
环境类
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Collections public static <T> void sort (List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c) list.sort(c); } ... }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class StrategyDemo public static void main (String[] args) List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.sort(list, new AscComparator()); } }
拒绝策略接口
1 2 3 public interface RejectedExecutionHandler void rejectedExecution (Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) }
默认拒绝策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler public AbortPolicy () public void rejectedExecution (Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() + " rejected from " + e.toString()); } }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public ThreadPoolExecutor (int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
排序算法是最常见的基本算法, 面试中经常会问到各种各样的排序。假如说我们的应用中需要用到不同时间复杂度的排序,是否可以用策略模式来实现呢?
策略接口
1 2 3 public interface SortStrategy void sort () }
策略实现类
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class BubbleSortStrategy implements SortStrategy @Override public void sort () System.out.println("冒泡排序" ); } }
上下文策略管理类
1 2 3 4 5 public class SortHandler void sort (SortStrategy strategy) strategy.sort(); } }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class StrategyDemo3 public static void main (String[] args) SortHandler sortHandler = new SortHandler(); sortHandler.sort(new BubbleSortStrategy()); } }
在Redis中有各种各样的缓存淘汰策略, 比如 LRU、LFU 等等, 这里用策略模式来模拟下相关实现。
策略接口
1 2 3 4 public interface CacheInvalidStrategy void invalid () }
LRU策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class LRUStrategy implements CacheInvalidStrategy @Override public void invalid () System.out.println("LRU" ); } }
上下文
1 2 3 4 5 public class RedisCache void setCacheStrategy (CacheInvalidStrategy cacheStrategy) cacheStrategy.invalid(); } }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class Demo4 public static void main (String[] args) RedisCache redisCache = new RedisCache(); redisCache.setCacheStrategy(new LRUStrategy()); } }
大家在项目中肯定经常用到缓存,假设某个场景中需要根据key动态选择缓存策略,其中一部分存储在JVM本地缓存,一部分需要存储在分布式缓存。
策略接口
1 2 3 public interface Cache boolean add (String key, Object object) }
本地缓存策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class CacheMemoryImpl implements Cache @Override public boolean add (String key, Object object) System.out.println("保存到map" ); return false ; } }
redis缓存策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 public class CacheRedisImpl implements Cache @Override public boolean add (String key, Object object) System.out.println("保存到Redis" ); return false ; } }
上下文对策略的管理达到动态切换缓存的目的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public class CacheManage private Cache cacheMemory = new CacheMemoryImpl(); private Cache cacheRedis = new CacheRedisImpl(); void putChche (String key, Object value) if (key.contains("local" )) { cacheMemory.add(key, value); } else { cacheRedis.add(key, value); } } }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class CacheService public static void main (String[] args) CacheManage cacheManage = new CacheManage(); cacheManage.putChche("local-key" , "value" ); } }
假设项目中的重要数据需要备份,一般需要压缩归档。但是我们又不能把压缩算法写死了,比方说前期选型zip,后期可能觉得压缩比不够,需要切换成7z。
压缩策略接口
1 2 3 4 public interface CompressionStrategy void compress (Object data) }
zip压缩实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class ZipCompression implements CompressionStrategy @Override public void compress (Object data) System.out.println("zip压缩" ); } }
压缩器
1 2 3 4 5 public class Compressor void compress (Object data, CompressionStrategy compressionStrategy) compressionStrategy.compress(data); } }
备份服务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class CompressService public static void main (String[] args) Compressor compressor = new Compressor(); compressor.compress(new Object(), new ZipCompression()); } }
物联网场景中,传感器上报的数据经常有各种各样的协议和对应的加密算法,我们需要根据上行消息中的固定报文字段进行解码。
解密策略接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface DecryptStrategy String type () ; void decrypt () }
base64解密策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Component("base64Strategy") public class Base64Strategy implements DecryptStrategy public String type () return "BASE64" ; } @Override public void decrypt () System.out.println("--BASE64策略模式---" ); } }
解密处理上下文
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Component public class DecryptHandler implements ApplicationContextAware private Map<String, DecryptStrategy> strategyMap = new HashMap<>(); public DecryptHandler () public void decrypt (String type) DecryptStrategy strategy = strategyMap.get(type); strategy.decrypt(); } @Override public void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException Map<String, DecryptStrategy> beansOfType = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(DecryptStrategy.class); for (DecryptStrategy bean : beansOfType.values()) { strategyMap.put(bean.type(), bean); } System.out.println(beansOfType.size()); } }
应用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @SpringBootTest @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) public class DecryptHandlerTest @Autowired DecryptHandler decryptHandler; @Test public void test () decryptHandler.decrypt("MD5" ); } }
做过电商项目的都知道促销模块可能会有不同的促销策略。
促销策略接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public interface PromotionStrategy void doPromotion () }
返现促销策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class FanxianPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy @Override public void doPromotion () System.out.println("返现促销" ); } }
满减促销策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class manjianPromotionStrategy implements PromotionStrategy @Override public void doPromotion () System.out.println("满减促销" ); } }
策略工厂类对策略进行管理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class PromotionStrategyFactory private static Map<String, PromotionStrategy> PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP = new HashMap<>(); static { PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.put(PromotionKey.MANJIAN, new LijianPromotionStrategy()); PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.put(PromotionKey.FANXIAN, new FanxianPromotionStrategy()); } private static final PromotionStrategy NON_PROMOTION = new EmptyPromotionStrategy(); private PromotionStrategyFactory () public static PromotionStrategy getPromotionStrategy (String promotionKey) PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy = PROMOTION_STRATEGY_MAP.get(promotionKey); return promotionStrategy == null ? NON_PROMOTION : promotionStrategy; } private interface PromotionKey String MANJIAN = "manjian" ; String FANXIAN = "fanxian" ; } }
上下文包装策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class PromotionActivity private PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy; public PromotionActivity (PromotionStrategy promotionStrategy) this .promotionStrategy = promotionStrategy; } public void executePromotionStrategy () promotionStrategy.doPromotion(); } }
对外应用提供策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class PromotionStrategyTest public static void main (String[] args) String promotionKey = "lijian" ; PromotionActivity promotionActivity = new PromotionActivity( PromotionStrategyFactory.getPromotionStrategy(promotionKey)); promotionActivity.executePromotionStrategy(); } }
一般项目中涉及到文件存储的部分,要么是存储在类似与阿里的OSS,要么是自己基于 FastDFS 搭建分布式存储系统。如果我们条件有限,但是又需要后期可扩展,那么这里可以用策略模式实现。
策略接口
1 2 3 public interface FileUpload void upload (MultipartFile file) }
FastDFS策略实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class FastDFSUpload implements FileUpload @Override public void upload (MultipartFile file) System.out.println("FastDFS" ); } }
上下文文件管理
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class FileManage void upload (MultipartFile file, FileUpload fileUpload) fileUpload.upload(file); } }
应用接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class FileService public static void main (String[] args) FileManage fileManage = new FileManage(); fileManage.upload(null , new FastDFSUpload()); } }
本文到此结束, 感谢您的阅读。如果您觉得有所帮助, 请关注公众号【当我遇上你】, 并分享给身边的小伙伴。您的支持是我持续写作的最大动力。