学习ConcurrentHashMap1.7分段锁原理
接上一篇 学习ConcurrentHashMap1.8并发写机制 , 本文主要学习 Segment分段锁 的实现原理。
虽然 JDK1.7 在生产环境已逐渐被 JDK1.8 替代,然而一些好的思想还是需要进行学习的。比方说位图中寻找 bit 位的思路是不是和 ConcurrentHashMap1.7 有点相似?
接下来,本文基于 OpenJDK7 来做源码解析。
ConcurrentHashMap中put()是线程安全的。但是很多时候, 由于业务需求, 需要先 get() 操作再 put() 操作,这2个操作无法保证原子性,这样就会产生线程安全 问题了。大家在开发中一定要注意。
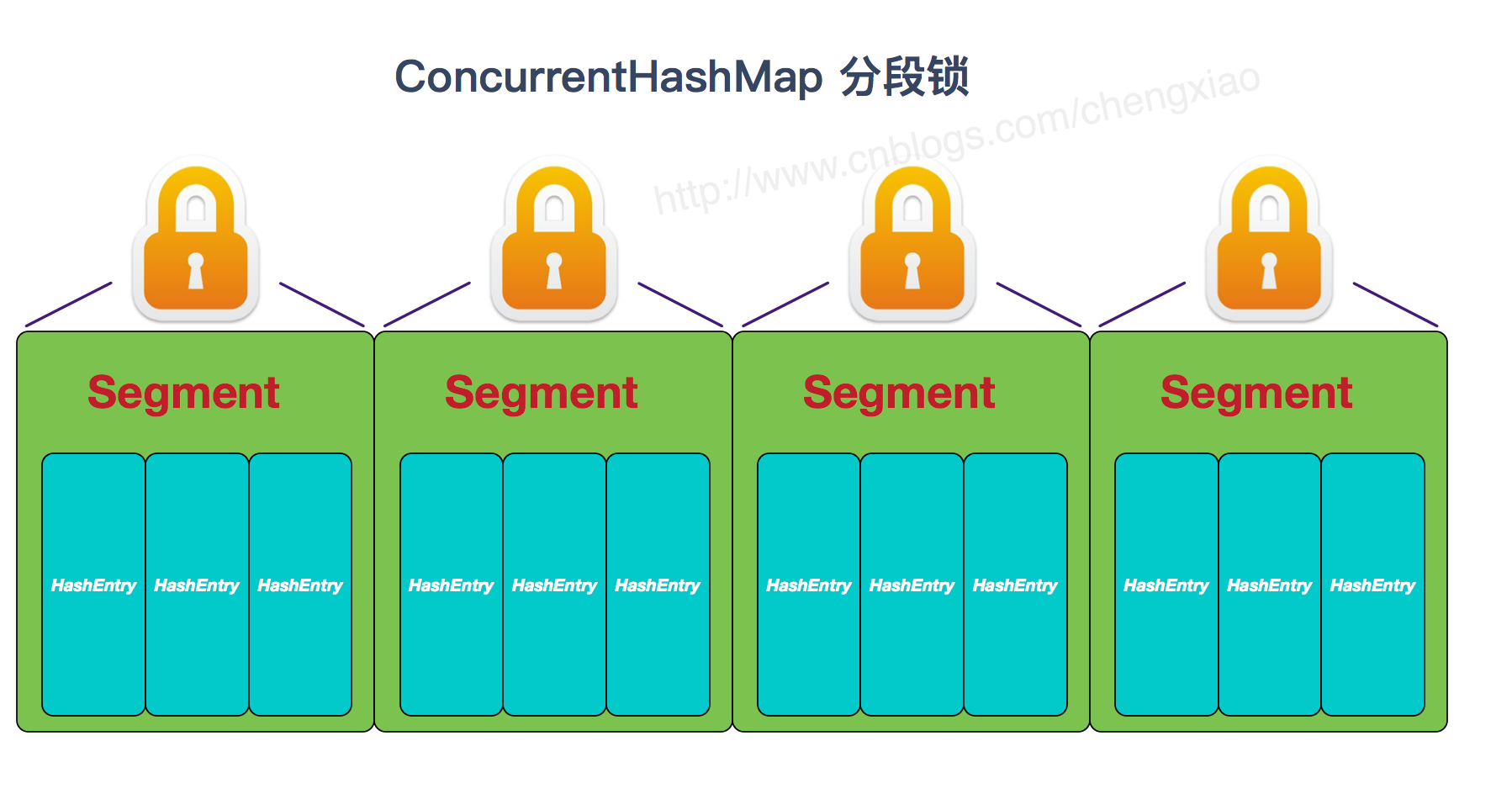
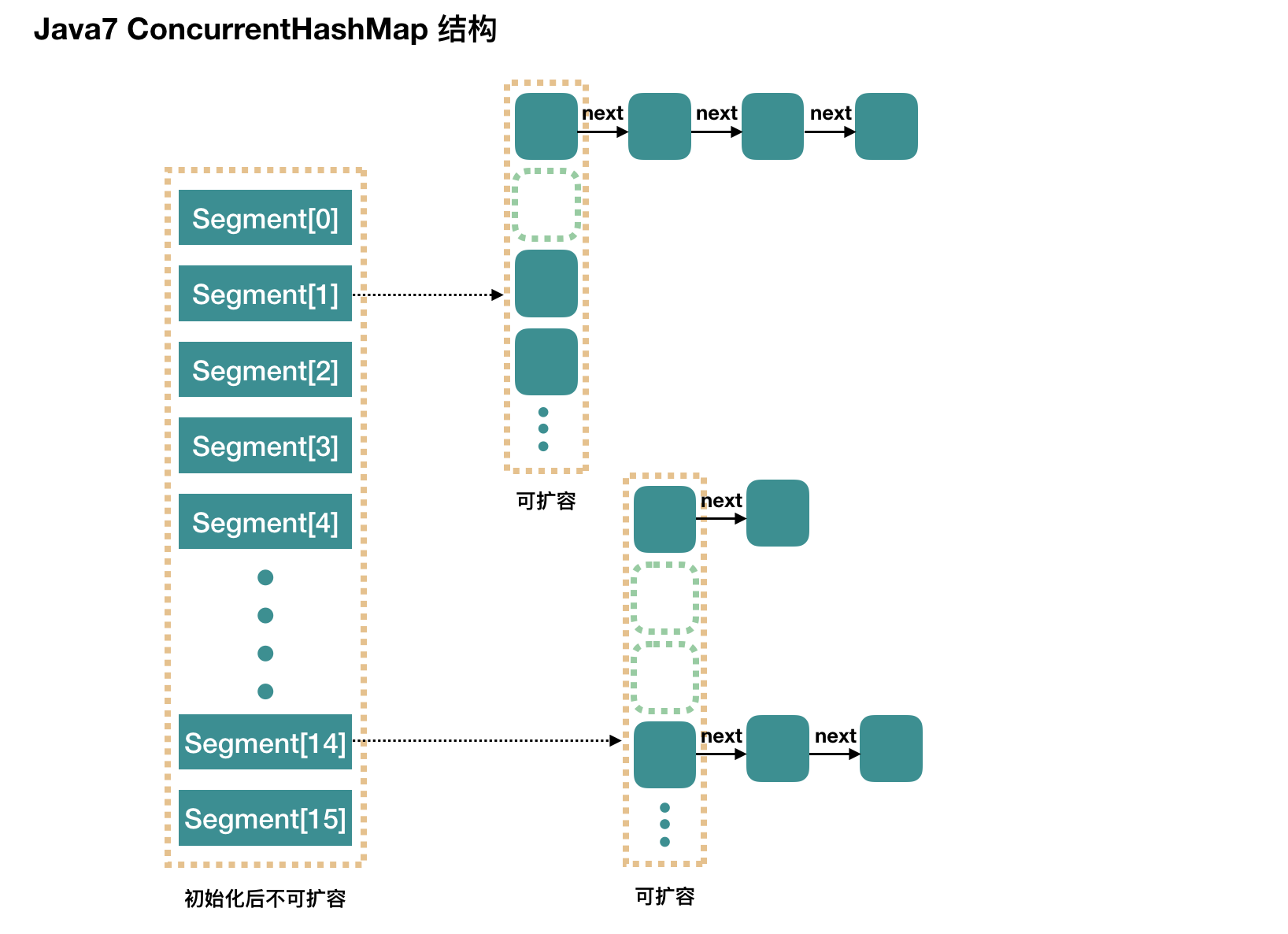
ConcurrentHashMap的结构示意图如下:
在进行数据的定位时,会首先找到 segment, 然后在 segment 中定位 bucket。如果多线程操作同一个 segment, 就会触发 segment 的锁 ReentrantLock, 这就是分段锁的基本实现原理 。
HashEntry 是 ConcurrentHashMap 的基础单元(节点),是实际数据的载体。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 static final class HashEntry <K ,V > final int hash; final K key; volatile V value; volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; HashEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry<K,V> next) { this .hash = hash; this .key = key; this .value = value; this .next = next; } final void setNext (HashEntry<K,V> n) UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(this , nextOffset, n); } static final sun.misc.Unsafe UNSAFE; static final long nextOffset; static { try { UNSAFE = sun.misc.Unsafe.getUnsafe(); Class k = HashEntry.class; nextOffset = UNSAFE.objectFieldOffset (k.getDeclaredField("next" )); } catch (Exception e) { throw new Error(e); } } }
Segment 继承 ReentrantLock 锁,用于存放数组 HashEntry[]。在这里可以看出, 无论1.7还是1.8版本, ConcurrentHashMap 底层并不是对 HashMap 的扩展, 而是同样从底层基于数组+链表进行功能实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 static final class Segment <K ,V > extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable private static final long serialVersionUID = 2249069246763182397L ; static final int MAX_SCAN_RETRIES = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1 ? 64 : 1 ; transient volatile HashEntry<K,V>[] table; transient int count; transient int modCount; transient int threshold; final float loadFactor; Segment(float lf, int threshold, HashEntry<K,V>[] tab) { this .loadFactor = lf; this .threshold = threshold; this .table = tab; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public ConcurrentHashMap (int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) if (!(loadFactor > 0 ) || initialCapacity < 0 || concurrencyLevel <= 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (concurrencyLevel > MAX_SEGMENTS) concurrencyLevel = MAX_SEGMENTS; int sshift = 0 ; int ssize = 1 ; while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) { ++sshift; ssize <<= 1 ; } this .segmentShift = 32 - sshift; this .segmentMask = ssize - 1 ; if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; int c = initialCapacity / ssize; if (c * ssize < initialCapacity) ++c; int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY; while (cap < c) cap <<= 1 ; Segment<K,V> s0 = new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int )(cap * loadFactor), (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0); this .segments = ss; }
由图和源码可知,当用默认构造函数时,最大并发数是16,即最大允许16个线程同步写操作,且无法扩展。所以如果我们的场景数据量比较大时,应该设置合适的并发数,避免频繁锁冲突。
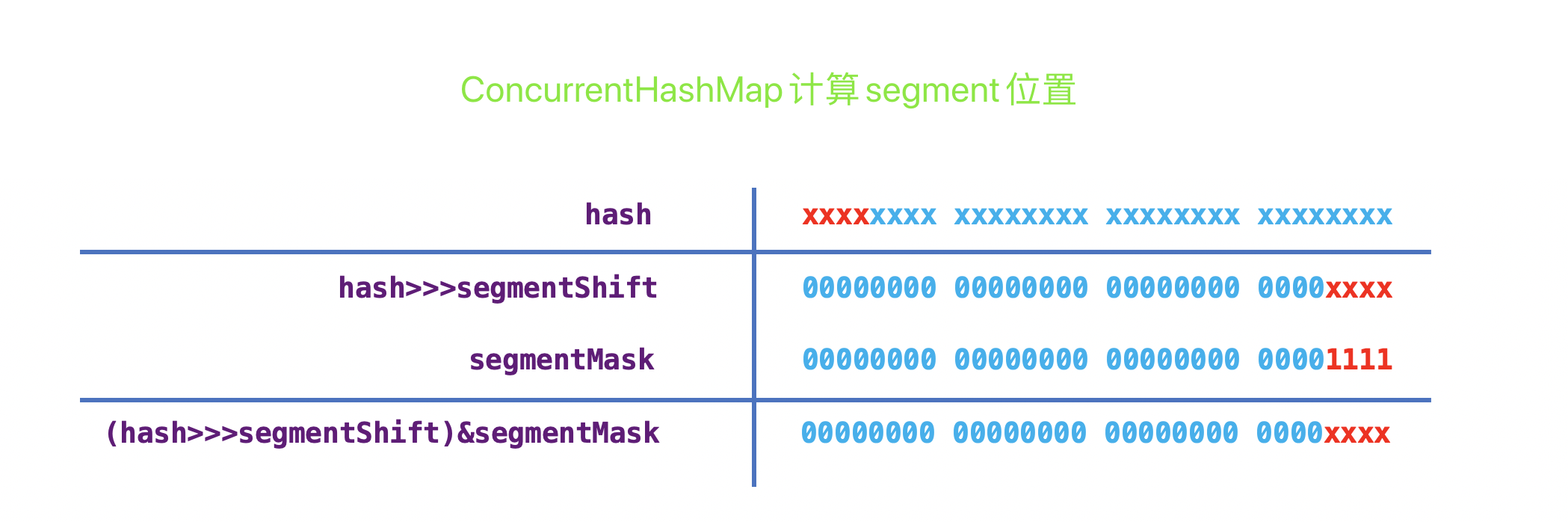
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public V put (K key, V value) Segment<K,V> s; if (value == null ) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = hash(key.hashCode()); int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask; if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject (segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null ) s = ensureSegment(j); return s.put(key, hash, value, false ); }
找出对应segment,如果不存在就创建并初始化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment (int k) final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this .segments; long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE; Segment<K,V> seg; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null ) { Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0 ]; int cap = proto.table.length; float lf = proto.loadFactor; int threshold = (int )(cap * lf); HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]; if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null ) { Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab); while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null ) { if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null , seg = s)) break ; } } } return seg; }
上一步找到segment位置后计算节点在segment中的位置。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 final V put (K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value); V oldValue; try { HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table; int index = (tab.length - 1 ) & hash; HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index); for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) { if (e != null ) { K k; if ((k = e.key) == key || (e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) { oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent) { e.value = value; ++modCount; } break ; } e = e.next; } else { if (node != null ) node.setNext(first); else node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first); int c = count + 1 ; if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) rehash(node); else setEntryAt(tab, index, node); ++modCount; count = c; oldValue = null ; break ; } } } finally { unlock(); } return oldValue; }
如果加锁失败则先走 scanAndLockForPut() 方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut (K key, int hash, V value) HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this , hash); HashEntry<K,V> e = first; HashEntry<K,V> node = null ; int retries = -1 ; while (!tryLock()) { HashEntry<K,V> f; if (retries < 0 ) { if (e == null ) { if (node == null ) node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null ); retries = 0 ; } else if (key.equals(e.key)) retries = 0 ; else e = e.next; } else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) { lock(); break ; } else if ((retries & 1 ) == 0 && (f = entryForHash(this , hash)) != first) { e = first = f; retries = -1 ; } } return node; }
(retries & 1) == 0 没理解是在做什么,有小伙伴看明白了请赐教。
本文到此结束,主要是学习分段锁是如何工作的。谢谢大家的观看。