Java面试必问之Hashmap底层实现原理(JDK1.7)
1. 前言
Hashmap可以说是Java面试必问的,一般的面试题会问:
- Hashmap有哪些特性?
- Hashmap底层实现原理(get\put\resize)
- Hashmap怎么解决hash冲突?
- Hashmap是线程安全的吗?
- …
今天就从源码角度一探究竟。笔者的源码是OpenJDK1.7
2. 构造方法
首先看构造方法的源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
transient Entry[] table;
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR;
threshold = (int)(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
init();
}
|
由以上源码可知,Hashmap的初始容量默认是16, 底层存储结构是数组(到这里只能看出是数组, 其实还有链表,下边看源码解释)。基本存储单元是Entry,那Entry是什么呢?我们接着看Entry相关源码,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> next;
final int hash;
Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) {
value = v;
next = n;
key = k;
hash = h;
}
...
}
|
由Entry源码可知,Entry是链表结构。综上所述,可以得出:
Hashmap底层是基于数组和链表实现的
3. Hashmap中put()过程
我已经将put过程绘制了流程图帮助大家理解
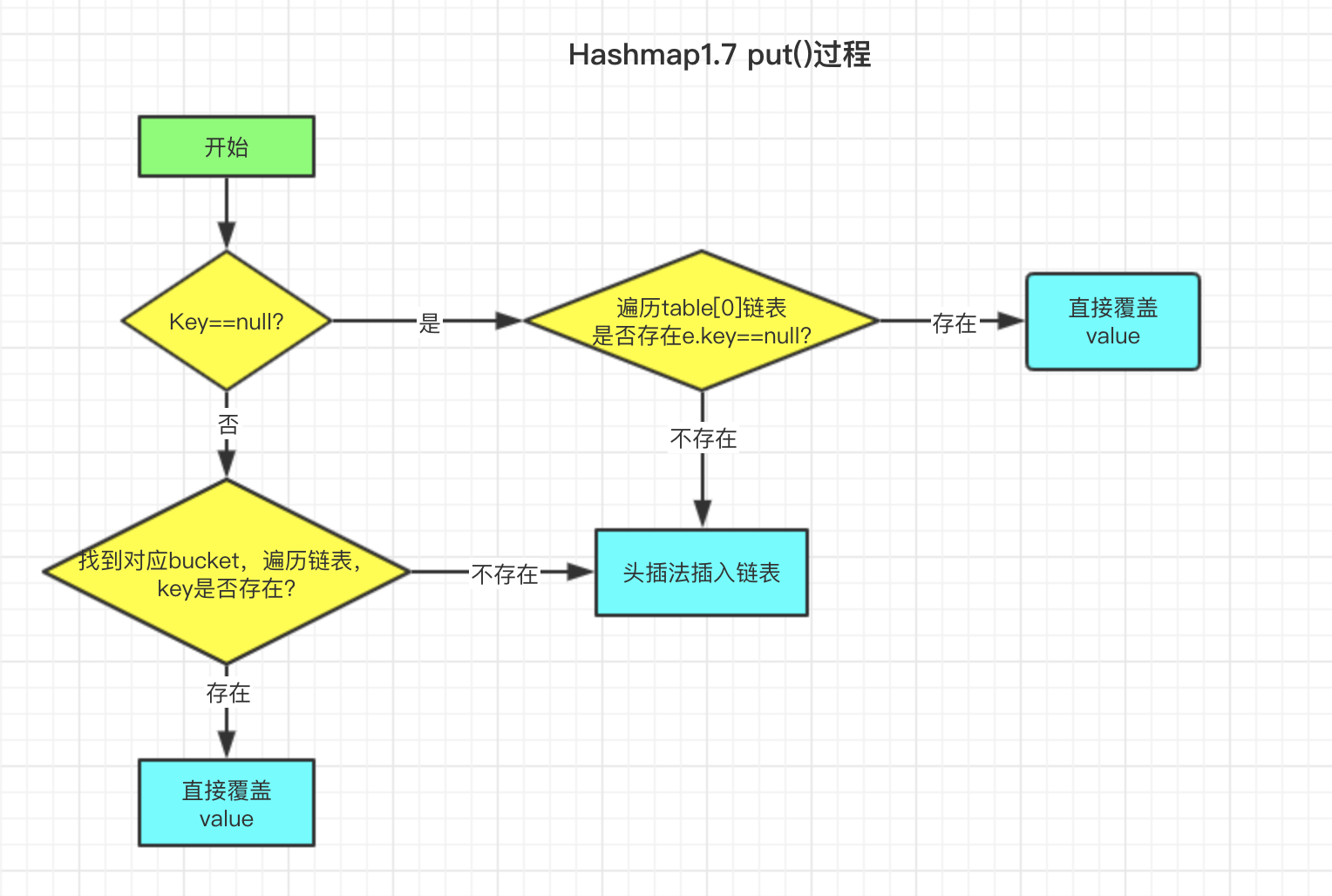
先上put源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
|
上图中多次提到头插法,啥是 头插法 呢?接下来看 addEntry 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
if (size++ >= threshold)
resize(2 * table.length);
}
|
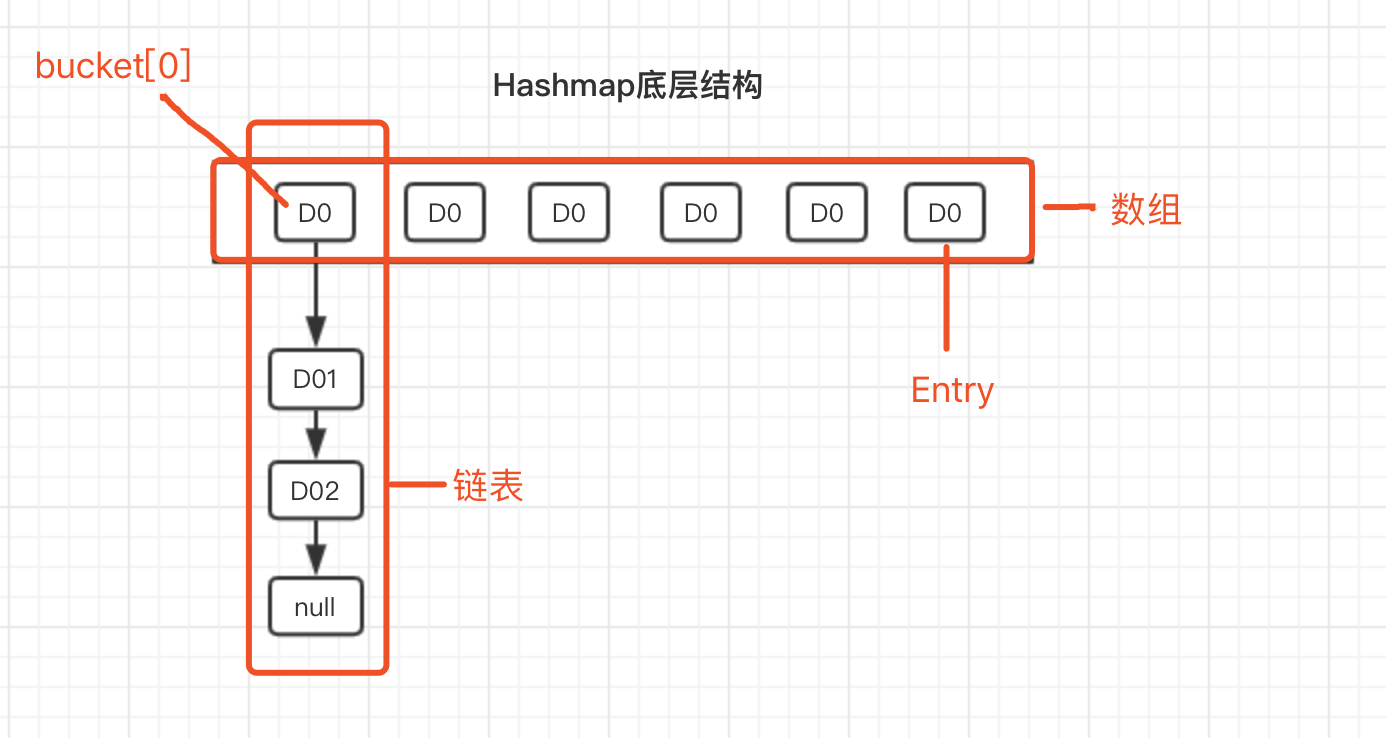
结合Entry类的构造方法,每次插入新元素的时候,将bucket原链表取出,新元素的next指向原链表,这就是 头插法 。为了更加清晰的表示Hashmap存储结构,再绘制一张存储结构图。
4. Hashmap中get()过程
get()逻辑相对比较简单,如图所示
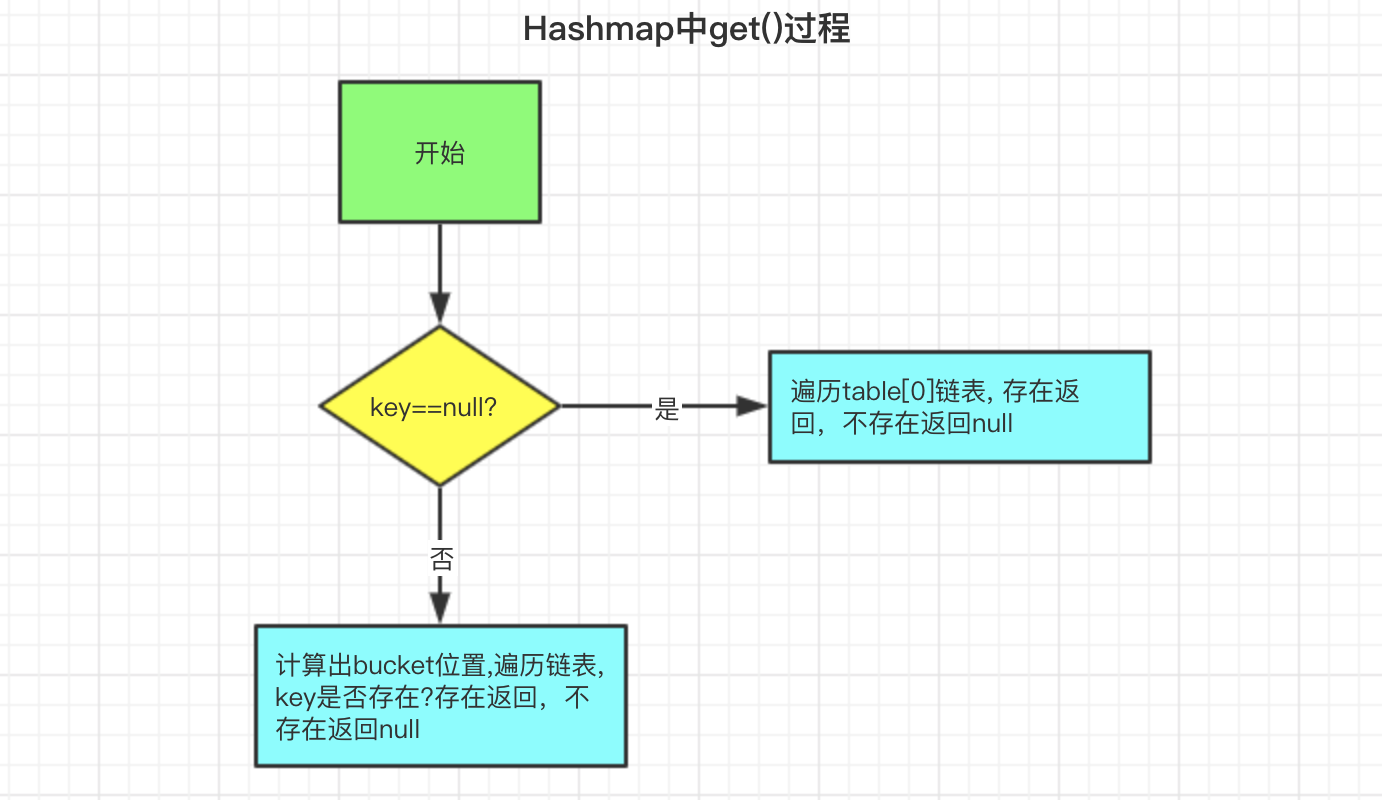
我们来对应下get()源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public V get(Object key) {
if (key == null)
return getForNullKey();
int hash = hash(key.hashCode());
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[indexFor(hash, table.length)];
e != null;
e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k)))
return e.value;
}
return null;
}
|
5. Hashmap中resize()过程
只要是新插入元素,即执行addEntry()方法,在插入完成后,都会判断是否需要扩容。从addEntry()方法可知,扩容后的容量为原来的2倍。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| void resize(int newCapacity) {
Entry[] oldTable = table;
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity];
transfer(newTable);
table = newTable;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
}
|
这里有个transfer()方法没讲,别着急,扩容时线程安全的问题出现在这个方法中,接下来讲解数组复制过程。
6. Hashmap扩容安全问题
大家都知道结果: 多线程扩容有可能会形成环形链表,这里用图给大家模拟下扩容过程。
首先看下单线程扩容的头插法
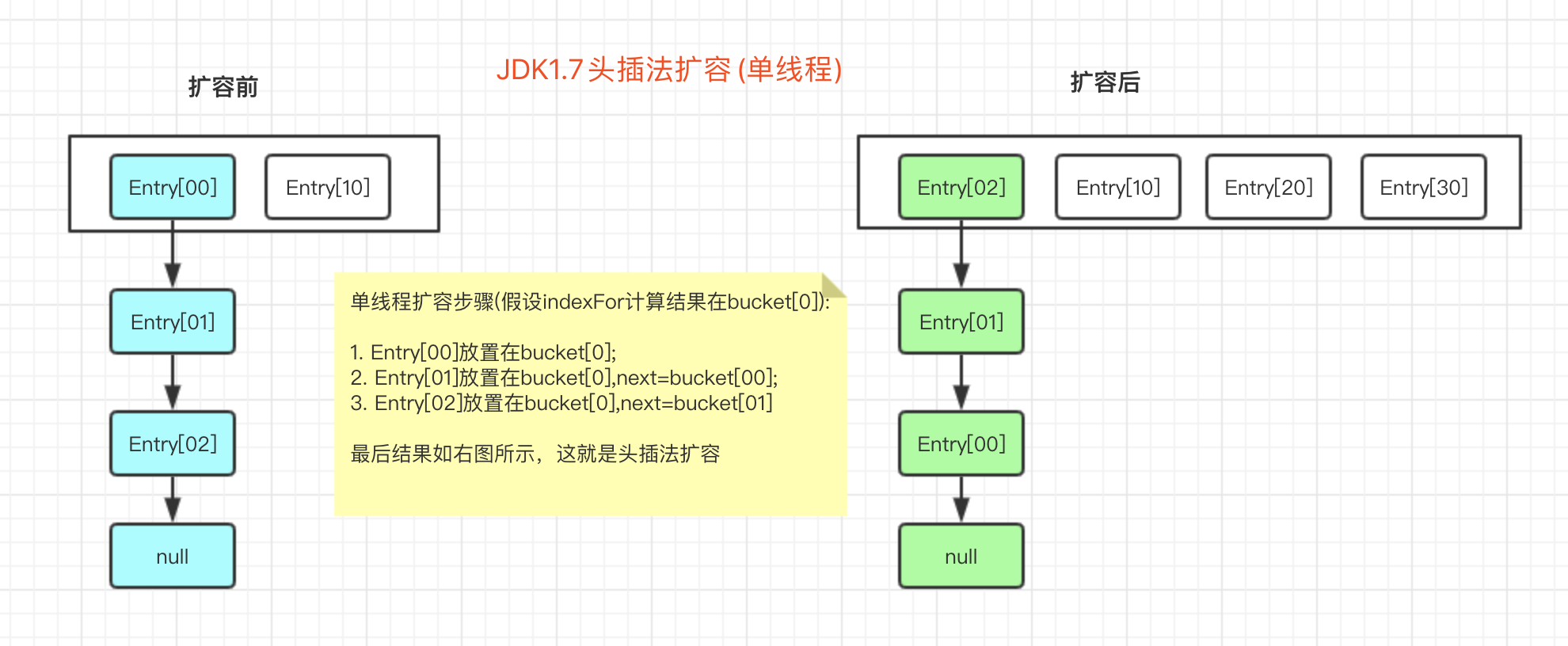
然后看下多线程可能会出现的问题
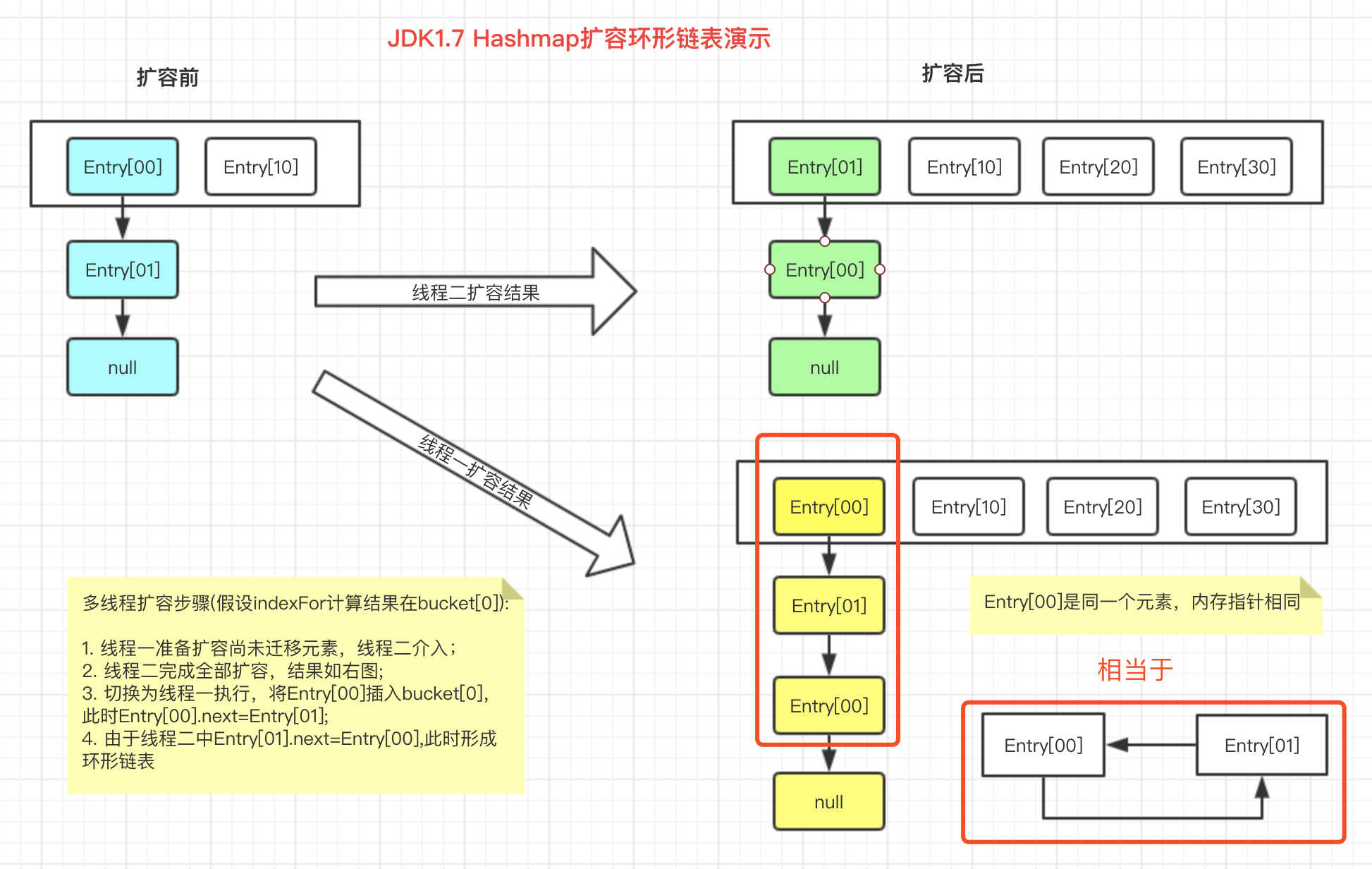
以下是源码,你仔细品一品
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table;
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) {
Entry<K,V> e = src[j];
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;
do {
Entry<K,V> next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity);
e.next = newTable[i];
newTable[i] = e;
e = next;
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
|
7. Hashmap寻找bucket位置
1
2
3
4
| static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
|
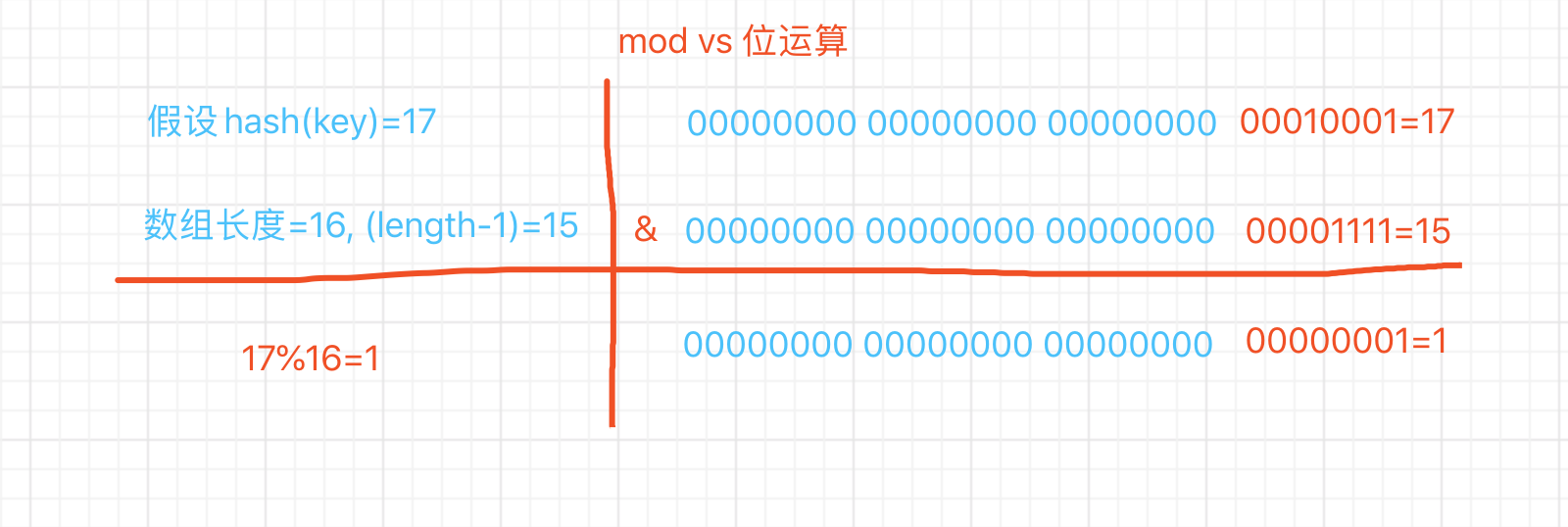
由源码可知, jdk根据key的hash值和数组长度做mod运算,这里用位运算代替mod。
hash运算值是一个int整形值,在java中int占4个字节,32位,下边通过图示来说明位运算。
8. AD
如果您觉得还行,请关注公众号【当我遇上你】, 您的支持是我输出的最大动力。
同时,欢迎大家一起交流学习。










